The Use of Carbon Fibre and Epoxy Resin for Engineered Repairs in Oil and Gas
Introduction
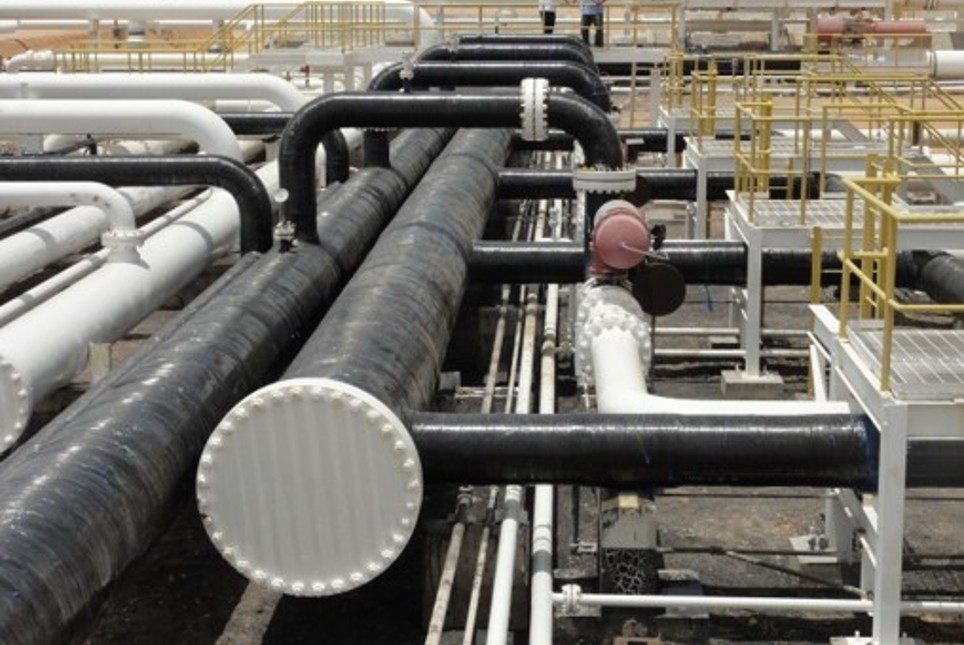
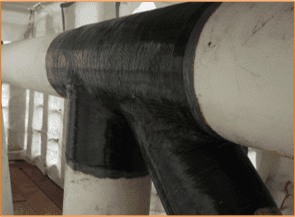
The oil and gas industry routinely encounters degradation of structural and pressure-retaining components due to corrosion, mechanical damage, and environmental exposure. Engineered composite repair systems using carbon fibre and epoxy resin have been developed as a technically robust solution for restoring integrity and extending service life without the need for intrusive interventions or hot work. These systems have been applied to a wide range of assets including topside structural components (such as decks, beams, and columns), pipework, onshore pipelines, and subsea pipeline systems.
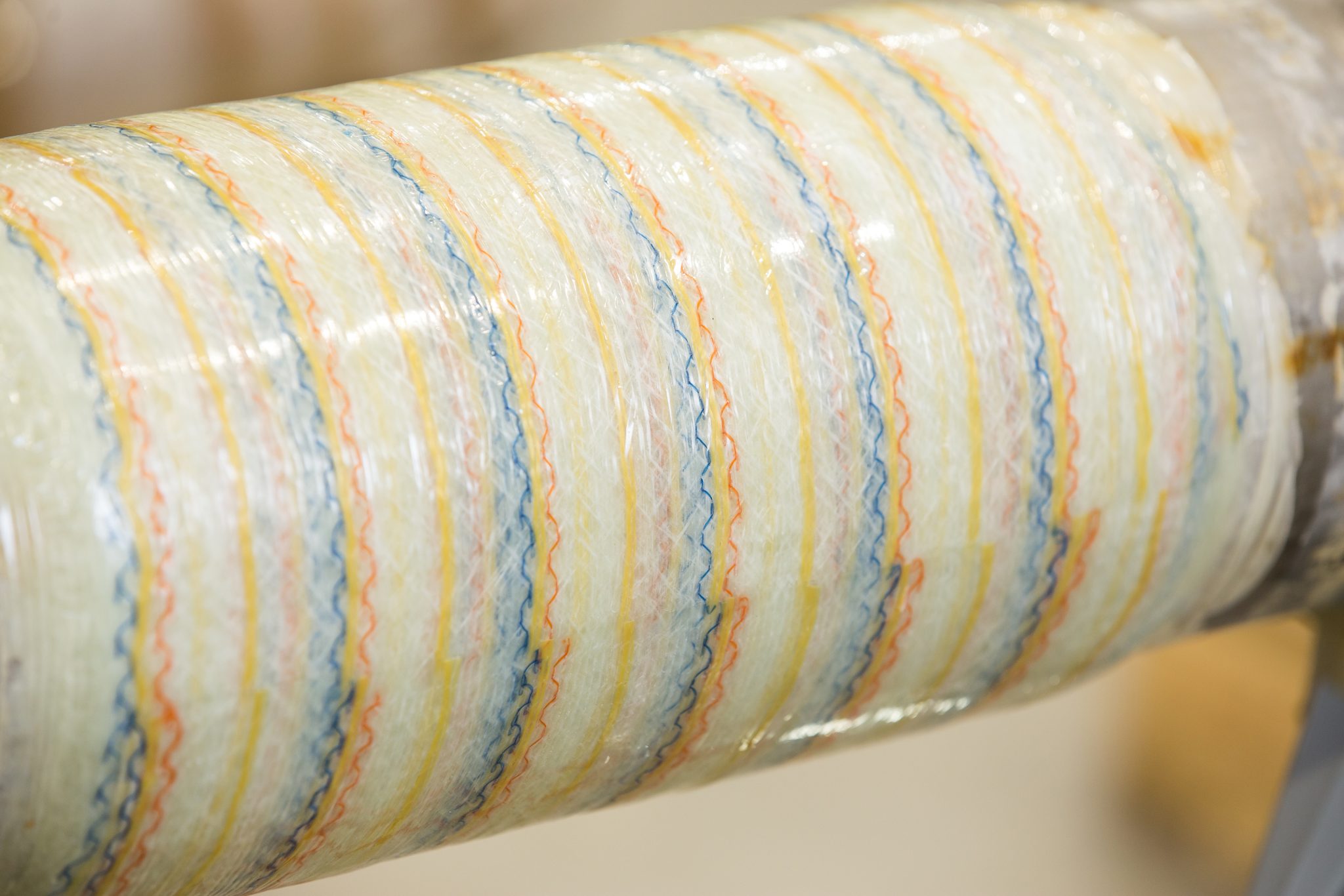
Carbon fibre is favoured for its high tensile modulus, greater than that of glass fibres with a near-zero coefficient of thermal expansion and its compatibility with a variety of epoxy resins, make it well-suited for both topside and underwater environments. Epoxy resins are the preferred matrix due to their strong adhesive properties to steel substrates and adaptability to diverse service conditions. Resin systems can be chemically modified for specific use cases: slower-reacting formulations for high ambient temperatures (e.g. Middle East), fast-curing systems for cold climates (e.g. North Sea), hydrophobic variants for subsea service, and core-shell toughened resins to enhance impact resistance in structural applications, specifically repairs to deck plates.


International Standards
Design and application of composite repairs are governed by international standards such as ISO 24817 and ASME PCC-2, with ongoing development of an API standard focused on structural composite repair.
Repair Types
For pipeline and pipework repairs, critical design inputs include internal pressure, defect type and geometry, pipe diameter and wall thickness. Repairs to structural components require a similar set of inputs; however instead of internal pressure, the applied loading must be considered. For example, a deck would be engineered for a uniformly distributed load, while a beam would require the applied bending moment.
Successful composite repair applications rely on trained technicians to carry out the application, correct surface preparation, controlled lay-up and extensive quality control checks. Post application integrity of the repair can then be verified and monitored by non-destructive testing, with focus areas on the composite material, looking for delaminations and most importantly, the bond line, to verify that there are no disbonded areas outside of the original defect area.
This article presents a technical overview of material selection, design methodology, qualification testing, and field experience with carbon fibre epoxy composite systems. It also discusses future developments in standardisation and material technologies supporting broader adoption across the oil and gas sector.
Interested in learning more about ICR’s composite repairs?
Please contact ICR’s Technical Director, Composites in Engineering, Gareth Urukalo (gareth.urukalo@icr-world.com). Otherwise, please use the links below to find out more about our technologies:
INSONO™ composite repair inspection
Send us your enquiry
Please complete the form below, and a member of our team will be in touch as soon as possible. Alternatively, please send your enquiry directly to sales@icr-world.com




